Gabapentin is a prescription medication used to treat adults with nerve pain caused by shingles. Shingles is a painful rash that is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the virus that also causes chickenpox. Gabapentin is also used in combination with other medications to treat partial seizures. Gabapentin belongs to a group of drugs called anticonvulsants, which help treat seizures by decreasing abnormal excitement in the brain. It also works by altering the way the body senses pain.
This medication comes in tablet, capsule, and oral (by mouth) solution forms and is taken up to 3 times a day, with or without food. The capsules are taken with a full glass of water.
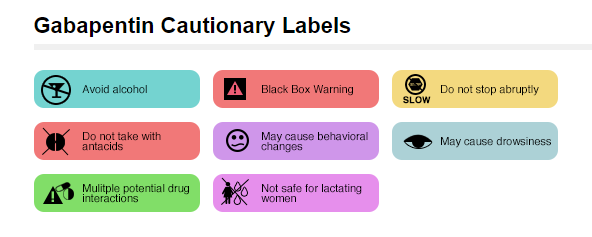
Common side effects of gabapentin include lack of coordination, dizziness, and drowsiness. Do not drive a car or operate heavy machinery until you know how this medication affects you.
Gabapentin Cautionary Labels
Uses of Gabapentin
Gabapentin is a prescription medicine used to treat:
- Pain from damaged nerves (postherpetic pain) that follows healing of shingles (a painful rash that comes after a herpes zoster infection) in adults.
- Partial seizures when taken together with other medicines in adults and children 3 years of age and older.
This medication may be prescribed for other uses. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Gabapentin Brand Names
Gabapentin may be found in some form under the following brand names:
-
Fanatrex
-
Gabarone
-
Gralise
-
Horizant
-
Neurontin
Gabapentin Drug Class
Gabapentin is part of the drug class:
-
Other antiepileptics
Gabapentin Precautions
Do not stop taking gabapentin without first talking to your healthcare provider.
Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems.
Gabapentin can cause serious side effects including:
- 1. Like other antiepileptic drugs, gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500.
- Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempts to commit suicide
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- feeling agitated or restless
- panic attacks
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- new or worse irritability
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
How you can watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions:
- Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled.
Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you are worried about symptoms.
Do not stop taking gabapentin without first talking to a healthcare provider.
- Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems. Stopping a seizure medicine suddenly in a patient who has epilepsy can cause seizures that will not stop (status epilepticus).
Suicidal thoughts or actions can be caused by things other than medicines. If you have suicidal thoughts or actions, your healthcare provider may check for other causes.
- 2. Changes in behavior and thinking – Using gabapentin in children 3 to 12 years of age can cause emotional changes, aggressive behavior, problems with concentration, restlessness, changes in school performance, and hyperactivity.
- 3. Gabapentin may cause a serious or life-threatening allergic reaction that may affect your skin or other parts of your body such as your liver or blood cells. You may or may not have a rash when you get this type of reaction. It may cause you to be hospitalized or to stop gabapentin. Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
-
- skin rash
- hives
- fever
- swollen glands that do not go away
- swelling of your lip and tongue
- yellowing of your skin or of the whites of the eyes
- unusual bruising or bleeding
- severe fatigue or weakness
- unexpected muscle pain
- frequent infections
These symptoms may be the first signs of a serious reaction. A healthcare provider should examine you to decide if you should continue taking gabapentin.
Do not take gabapentin if you are allergic to gabapentin or any of the other ingredients in gabapentin.
Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking gabapentin without first talking with your healthcare provider. Taking gabapentin with alcohol or drugs that cause sleepiness or dizziness may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse.
Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how gabapentin affects you. Gabapentin can slow your thinking and motor skills.